Blockchain Architecture: What Business Leaders Need to Know About Digital Asset Security
March 25, 2025
In today's digital economy, businesses are increasingly exploring blockchain technology to secure assets, streamline operations, and build trust with customers. But what makes blockchain systems reliable enough to handle millions or even billions in digital assets?
The answer lies in blockchain architecture—the underlying design principles that ensure security, transparency, and reliability. At Cobo, we've safeguarded businesses' digital assets by building custody solutions rooted in proven blockchain security principles, ensuring institutional-grade protection.
This guide will walk you through the essentials of blockchain architecture, explaining why each component matters for your business and how understanding these fundamentals can help you make better decisions about digital asset management.
The Building Blocks: Understanding Core Components
The Network: Strength in Numbers
Imagine a traditional database housed in a single location—if that location experiences a problem, your entire system could go down. Blockchain takes a different approach by spreading information across many computers (called nodes) around the world.
This distributed network creates resilience that businesses depend on. When one node fails, the system continues operating through the others. For businesses managing digital assets, this means no single point of failure can compromise your holdings.
Different nodes serve different purposes. Some store the complete history of all transactions, while others focus on creating new blocks or providing specialized services. This division of labor creates an ecosystem where each participant contributes to the overall security and efficiency of the network.
Why it matters for your business: This distributed approach means your digital assets don't depend on any single entity or system. Even if some parts of the network experience problems, your assets remain secure and accessible through other parts of the network.
Consensus Mechanisms: Building Trust Among Strangers
One of blockchain's most revolutionary aspects is its ability to create trust without requiring participants to know or trust each other. This happens through consensus mechanisms—the rules that all participants follow to agree on transaction validity.
Think of consensus mechanisms as the voting systems that determine which transactions get added to the blockchain. Different blockchain networks use different approaches: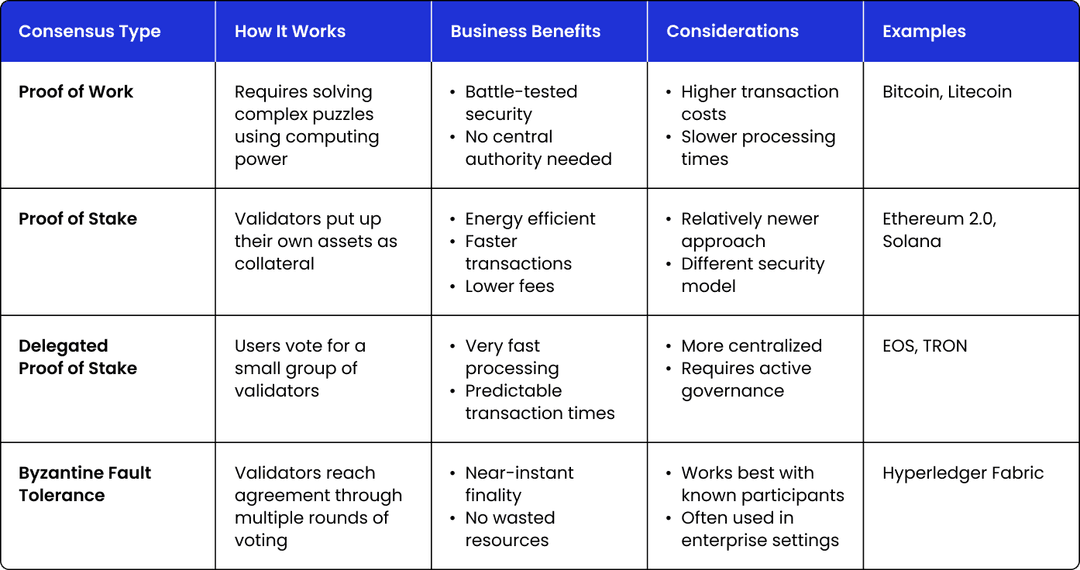
Why it matters for your business: The consensus mechanism directly impacts transaction speed, costs, and security guarantees. Businesses handling high-value transactions might prioritize security (favoring Proof of Work), while those needing fast, frequent transactions might prefer Proof of Stake or its variations.
Smart Contracts: Self-Executing Business Logic
Smart contracts represent one of blockchain's most powerful business applications. These are essentially digital agreements that automatically execute when specific conditions are met—no intermediaries required.
For example, a smart contract could automatically release payment to a supplier when a shipment's tracking data confirms delivery. This automation reduces administrative overhead and eliminates the need for trust between parties.
However, smart contracts must be implemented carefully. Since they execute automatically and are typically irreversible, errors in their code can have significant consequences. Proper testing and security audits are essential before deployment.
Why it matters for your business: Smart contracts can streamline operations, reduce costs, and create new business models by automating complex processes that traditionally required intermediaries. They're particularly valuable for financial services, supply chain management, and digital asset governance.
How Transactions Work: The Journey from Click to Confirmation
Understanding how transactions move through a blockchain system helps clarify why certain security practices are essential for businesses handling digital assets.
From Creation to Confirmation: Following the Money
When someone initiates a blockchain transaction, it follows a predictable path:
Transaction Creation: The sender creates a transaction specifying the recipient, amount, and any other necessary data. They digitally sign this information with their private key, proving their authorization without revealing sensitive details.
Network Broadcasting: The signed transaction is sent to the blockchain network, where it's relayed between nodes until it reaches a wide audience. At this stage, the transaction is "pending"—visible but not yet confirmed.
Verification Process: Network participants verify that the transaction follows all the rules: the sender has sufficient funds, the signature is valid, and the format is correct.
Block Addition: Verified transactions are bundled into "blocks" that get added to the blockchain through the consensus mechanism we discussed earlier. Once added, the transaction receives its first confirmation.
Growing Certainty: Each new block added to the chain provides an additional confirmation for older transactions. More confirmations mean greater security, as reversing the transaction becomes exponentially more difficult.
Why it matters for your business: This process creates the security and irreversibility that make blockchain valuable for business applications. Understanding the confirmation process helps businesses determine appropriate waiting periods before considering transactions final—typically more confirmations for higher-value transactions.
Withdrawal Systems: Where Security Meets Usability
For businesses managing digital assets, one of the most critical processes is the withdrawal system—how assets move from secure storage to their intended destinations. This is where security architecture faces its greatest test.
Balancing Protection with Accessibility
A well-designed withdrawal system incorporates multiple security layers without creating excessive friction for legitimate business operations:
Multi-factor Authentication Rather than relying on passwords alone, modern systems require multiple forms of verification before processing withdrawals. This typically combines something you know (password), something you have (mobile device), and sometimes something you are (biometric verification).
Verification Checks Before processing, each withdrawal request undergoes multiple checks: Is there sufficient balance? Does the request fall within established limits? Is the destination address properly formatted and on an approved list?
Graduated Approval Requirements As withdrawal amounts increase, so should security requirements. Small, routine transactions might process automatically, while larger amounts trigger additional approvals from multiple authorized personnel.
Time-Based Security Implementing waiting periods for large withdrawals or new recipient addresses provides time to detect and stop unauthorized transactions before they complete.
Why it matters for your business: These security measures protect your digital assets while maintaining operational efficiency. The right balance depends on your specific needs—a trading operation needs different parameters than a long-term treasury management system.
Behind the Scenes: Operational Security
While blockchain itself provides certain security guarantees, the systems interacting with blockchain require rigorous security practices.
Protecting the Keys to the Kingdom
In blockchain systems, private keys control access to assets. Protecting these keys requires comprehensive security measures:
Encryption at Every Level All sensitive data, especially private keys, should be encrypted both in storage and during transmission. This creates multiple layers of protection against unauthorized access.
Strict Access Controls Well-designed systems limit who can access different functions and information, following the principle of "least privilege"—granting only the minimum access necessary for each role.
Continuous Monitoring Advanced systems continuously monitor for unusual activities that might indicate security problems, allowing for rapid response to potential threats.
Incident Response Planning Even with the best preventive measures, businesses need clearly defined procedures for responding to security incidents when they occur.
Why it matters for your business: The strongest blockchain in the world can't protect assets if the systems interacting with it are compromised. Operational security measures ensure that the security promises of blockchain technology extend to your entire digital asset management system.
Looking Ahead: Evolving Blockchain Architecture
Blockchain technology continues to evolve, with new approaches addressing current limitations while maintaining core security principles.
Scaling for Enterprise Needs
As businesses adopt blockchain technology, performance requirements increase. Several approaches are addressing these needs:
Layer 1 Solutions improve the base blockchain itself through technical upgrades that increase transaction capacity.
Layer 2 Solutions build additional frameworks on top of existing blockchains to handle transactions more efficiently, while still benefiting from the security of the underlying blockchain.
Why it matters for your business: These scaling solutions are making blockchain more viable for high-volume business applications like payments, trading, and supply chain management.
Meeting Compliance Requirements
Modern blockchain systems increasingly incorporate regulatory compliance into their design:
Built-in Monitoring detects potentially suspicious activities to support anti-money laundering (AML) efforts.
Identity Integration allows for know-your-customer (KYC) verification while still maintaining appropriate privacy.
Comprehensive Audit Trails provide the transparency and accountability that regulators and business partners expect.
Why it matters for your business: These compliance features help businesses navigate regulatory requirements while still leveraging blockchain's advantages, reducing compliance costs and regulatory risks.
Conclusion: Building on Solid Foundations
Blockchain architecture provides the foundation for secure, efficient digital asset management. Understanding these architectural principles helps business leaders make informed decisions about custody solutions and blockchain implementations.
At Cobo, our digital asset custody platform builds on these architectural fundamentals, delivering institutional-grade security while supporting the operational needs of modern businesses. We incorporate multiple security layers, comprehensive monitoring, and flexible controls that adapt to your specific business requirements.
As blockchain technology continues to mature, we remain committed to evolving our security architecture and sharing knowledge with the business community through resources like this guide.
View more

Cold Wallet vs Hot Wallet: What Crypto Exchanges and Users Need to Know in 2025
June 17, 2025

Stablecoin Payments 101 for PSPs: How to Integrate Digital Dollars Without Rebuilding Your Stack
June 17, 2025

Cobo vs. Fireblocks: Choosing the Right Digital Asset Custody Provider for Your Business
June 17, 2025